Difference between revisions of "Ship Kelvin Wake"
m (→Kelvin wake) |
|||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | = | + | {{Ocean Wave Interaction with Ships and Offshore Structures |
| + | | chapter title = Ship Kelvin Wake | ||
| + | | next chapter = [[Linear Wave-Body Interaction]] | ||
| + | | previous chapter = [[Wavemaker Theory]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | + | {{incomplete pages}} | |
| − | + | = Introduction = | |
| − | |||
| − | = | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Wake.avon.gorge.arp.750pix.jpg|thumb|right|450px|Wake created behind a ship]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | A ship moving over the surface of undisturbed water sets up waves emanating from the bow and stern of the ship. The waves created by the ship consist of divergent and transverse waves. The divergent wave are observed as the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wake wake] of a ship with a series of diagonal or oblique crests moving outwardly from the point of disturbance. These wave were first studied by [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lord_Kelvin Lord Kelvin] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == Translating Coordinate System == | |
| − | <center><math> \ | + | We have a the standard fixed coordinate system <math>x, y, z</math> and a moving coordinate systems |
| + | which is moving in the <math>x</math> direction with speed <math>U</math>. We denote the moving coordinate | ||
| + | systems in the <math>x</math> direction by | ||
| + | <center><math> | ||
| + | \bar{x} = x + U t | ||
| + | </math></center> | ||
| − | + | Let <math> \Phi(\mathbf{x},t) \,</math> be the velocity potential describing the potential flow | |
| + | generated by the ship relative to the earth frame. | ||
| + | The same potential expressed relative to the ship frame is <math> \bar{\Phi}(\mathbf{\bar{x}},t) \, </math>. | ||
| + | The relation between the two potentials is given by the identity | ||
| + | <center><math> \Phi(x,y,z,t) = \bar{\Phi}(\bar{x},y,z,t) | ||
| + | = \bar{\Phi}(x-Ut,y,z,t) \,</math></center> | ||
| + | where the relation between the coordinates of the two coordinate systems has been introduced. | ||
| + | Note the time dependence occurs in two places in <math> \bar{\Phi} \,</math> and in one place in <math> \Phi \,</math>. The governing equations are always derived relative to the earth coordinate system and time derivatives are initially taken on <math> \Phi \, </math>. | ||
| + | Therefore | ||
| + | <center><math> \frac{\mathrm{d}\Phi}{\mathrm{d}t} = \frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d}t} \bar{\phi} ( x-Ut,y,z,t) | ||
| + | = \frac{\partial\phi}{\partial t} - U \frac{\partial\phi}{\partial x} </math></center> | ||
| − | < | + | All time derivatives of the earth fixed velocity potential <math> \Phi \, </math> which appear in the free surface condition and the Bernoulli equation can be expressed in terms of derivatives of <math> \bar{\Phi} \, </math> using the Galilean transformation derived above. |
| − | <center><math> \frac{\ | + | If the flow is steady relative to the ship fixed coordinate system |
| + | <center><math> \frac{\partial\bar{\Phi}}{\partial t} = 0 \, </math></center> | ||
| + | but | ||
| + | <center><math> \frac{\mathrm{d}\Phi}{\mathrm{d}t} = -U \frac{\partial\bar{\Phi}}{\partial x} \,</math></center> | ||
| + | or, the ship wake is stationary relative to the ship but not relative to an observed on the beach. | ||
| − | + | == Kelvin wake == | |
| − | + | [[Image:Kelvin_wake.jpg|thumb|right|600px|Diagram of the Kelvin Wake]] | |
| − | + | Local view of Kelvin wake consists approximately of a [[Linear Plane Progressive Regular Waves| plane progressive wave group]] propagating in direction <math> \theta\,\!</math>. | |
| + | As noted above surface wave systems of general form always consist of combinations of plane progressive waves of different frequencies and directions. The same model will apply to the ship kelvin wake. | ||
| + | Relative to the earth frame, the local plane wave in [[Infinite Depth]] takes the form | ||
| − | + | <center><math> \Phi = \frac{\mathrm{i}gA}{\omega} e^{kz-\mathrm{i}k(x\cos\theta+y\sin\theta)+ \mathrm{i}\omega t} </math></center> | |
| − | Relative to the | + | Relative to the ship frame |
| + | <center><math>bar{\Phi} = \frac{igA}{\omega} e^{kz-\mathrm{i}k(x\cos\theta+y\sin\theta)-\mathrm{i}(kU\cos\theta-\omega)t} </math></center> | ||
| − | + | But relative to the ship frame waves are stationary, so we must have: | |
| + | <center><math> kU\cos\theta = \omega \,</math></center> | ||
or | or | ||
| + | <center><math> \frac{\omega}{k} = C_p = U \cos \theta \, </math></center> | ||
| + | This implies the following | ||
| + | * The phase velocity of the waves in the kelvin wake propagating in direction <math>\theta\,</math> must be equal to <math> U\cos\theta\,</math>, otherwise they cannot be stationary relative to the ship. | ||
| + | * Relative to the earth system the frequency of a local system propagating in direction <math> \theta \, </math> is given by the relation <math> \omega = kU \cos \theta \, </math> | ||
| − | <center><math> | + | Relative to the earth system the [[Infinite Depth]] [[Dispersion Relation for a Free Surface]] states |
| + | <center><math> \omega^2 = g k \, </math></center> | ||
| + | so that | ||
| + | <center><math> \lambda(\theta) = \frac{2\pi U^2 \cos^2 \theta}{g} \, </math></center> | ||
| − | + | This is the wavelength of waves in a Kelvin wake propagating in direction <math> \theta \, </math> which | |
| + | are stationary relative to the ship. | ||
| − | + | == Application of the Group velocity == | |
| − | + | An observer sitting on an earth fixed frame observes a local wave system propagating in direction <math> \theta\,</math> travelling at its [[Wave Energy Density and Flux|group velocity]] <math>\frac{d\omega}{dK}\,</math> by virtue of the Rayleigh device which states that we need to focus on the speed of the energy density (<math> \sim \, </math> wave amplitude) rather than the speed of wave crests. So, relative to the earth fixed inclined coordinate system <math> (X', Y') \,</math>: | |
| − | + | <center><math> \frac{X'}{t} = V_g = \frac{d\omega}{dK} \, </math></center> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <center><math> \frac{ | ||
Or | Or | ||
| − | <center><math> X' = \frac{d\omega}{dK} t \ \Longrightarrow \ \frac{d}{dK} (K | + | <center><math> X' = \frac{d\omega}{dK} t \ \Longrightarrow \ \frac{d}{dK} (K X' - \omega t) = 0 </math></center> |
<center><math> X' = X \cos \theta + Y \sin \theta = x \cos\theta + y\sin\theta + Ut \cos\theta \,</math></center> | <center><math> X' = X \cos \theta + Y \sin \theta = x \cos\theta + y\sin\theta + Ut \cos\theta \,</math></center> | ||
| Line 63: | Line 88: | ||
So: | So: | ||
| − | <center><math> | + | <center><math> KX' - \omega t = K ( x\cos\theta + y\sin\theta ) + (KU\cos\theta - \omega) t \,</math></center> |
| − | + | However <math>(KU\cos\theta - \omega) t =0</math> so that the Rayleigh condition for the velocity of the group takes the form: | |
| − | |||
<center><math> \frac{d}{dK} [ K(\theta) (x\cos\theta + y\sin\theta) ] = 0 \, </math></center> | <center><math> \frac{d}{dK} [ K(\theta) (x\cos\theta + y\sin\theta) ] = 0 \, </math></center> | ||
| Line 71: | Line 95: | ||
By virtue of the dispersion relation derived above: | By virtue of the dispersion relation derived above: | ||
| − | <center><math> K(\theta) = \frac{g}{U^2 \cos^\theta} \, </math></center> | + | <center><math> K(\theta) = \frac{g}{U^2 \cos^2 \theta} \, </math></center> |
It follows from the chain rule of differentiation that Rayleigh's condition is: | It follows from the chain rule of differentiation that Rayleigh's condition is: | ||
| Line 79: | Line 103: | ||
At the position of the Kelvin waves which are locally observed by an observer at the beach. | At the position of the Kelvin waves which are locally observed by an observer at the beach. | ||
| − | * So the "visible" waves in the wake of a ship are <u>wave groups</u> which must travel at the local group velocity. These conditions translate into the above equation which will be solved and discussed next. More discussion and a more mathematical | + | * So the "visible" waves in the wake of a ship are <u>wave groups</u> which must travel at the local group velocity. These conditions translate into the above equation which will be solved and discussed next. More discussion and a more mathematical derivation based on the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Principle_of_stationary_phase principle of stationary phase] can be found in [[Newman 1977]]. |
| + | |||
| + | == Solution of the equation for angle == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Graphical_image.jpg|thumb|right|600px|Graphical image of the equations]] | ||
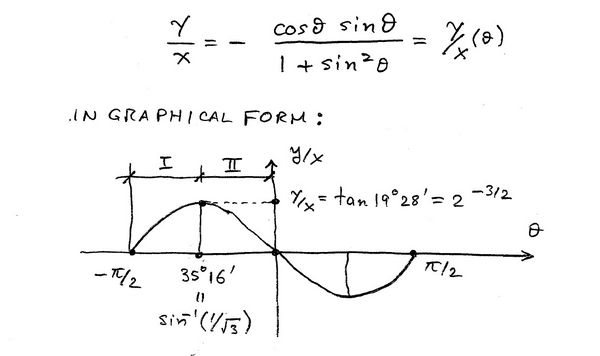
| − | The solution of the above equation will produce a relation between <math> \frac{y}{x} \,</math> and <math> \theta\,</math>. So local waves in a Kelvin wake can only propagate in a certain | + | The solution of the above equation will produce a relation between <math> \frac{y}{x} \,</math> and <math> \theta\,</math>. So local waves in a Kelvin wake can only propagate in a certain direction <math> \theta\,</math>, given <math> \frac{y}{x} \, </math>. |
Simple algebra leads to: | Simple algebra leads to: | ||
<center><math> \frac{y}{x} = - \frac{\cos\theta\sin\theta}{1+sin^2\theta} = \frac{y}{x}(\theta) | <center><math> \frac{y}{x} = - \frac{\cos\theta\sin\theta}{1+sin^2\theta} = \frac{y}{x}(\theta) | ||
| − | |||
</math></center> | </math></center> | ||
| − | + | which implies that | |
| − | * <math>\frac{y}{x}(\theta) \,</math> is anti-symmetric about <math> \theta = 0 \, </math> each | + | * <math>\frac{y}{x}(\theta) \,</math> is anti-symmetric about <math> \theta = 0 \, </math> and each part corresponds to the Kelvin wake in the port and starboard sides of the vessel. The physics on |
| − | |||
| − | part corresponds to the Kelvin wake in the port and starboard sides of the vessel. The physics on | ||
| − | |||
either side is identical due to symmetry. | either side is identical due to symmetry. | ||
| − | * <math> \theta = 0 \,</math>: waves propagating in the same direction as the ship. These waves | + | * <math> \theta = 0 \,</math>: waves propagating in the same direction as the ship. These waves can only exist at <math> Y = 0\, </math> as seen above. |
| − | + | * <math> \theta = \frac{\pi}{2} \, </math>: waves propagating at a <math> 90^\circ\,</math> angle relative to the ship direction of forward translation. | |
| − | * <math> \theta = \ | + | * <math> \theta = 35^\circ 16' \, </math>: (or 35,26°) waves propagating at an angle <math> \theta = 35^\circ 16' \, </math> relative to the ship axis. These are waves seen at the caustic of the Kelvin wake. |
| − | + | Let the solution of <math> \frac{y}{x}(\theta) \, </math> be of the form, when inverted: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Let the solution of | ||
<center><math> \mbox{Region I}: \qquad \theta = f_1 (\frac{y}{x}) \, </math></center> | <center><math> \mbox{Region I}: \qquad \theta = f_1 (\frac{y}{x}) \, </math></center> | ||
| Line 113: | Line 131: | ||
<center><math> \mbox{Region II}: \qquad \theta = f_2 (\frac{y}{x}) \, </math></center> | <center><math> \mbox{Region II}: \qquad \theta = f_2 (\frac{y}{x}) \, </math></center> | ||
| − | Note that observable waves cannot exist for values of <math> \frac{y}{x}\,</math> that exceed the | + | Note that observable waves cannot exist for values of <math> \frac{y}{x}\,</math> that exceed the value shown in the figure or <math> \left. \frac{y}{x} \right|_{Max} = 2^{-3/2} \,</math>. This translates into a value for the corresponding angle equal to <math> 19^\circ 28' \, </math> (or 19,47°) which is the angle of the caustic for any speed <math> U\,</math>. |
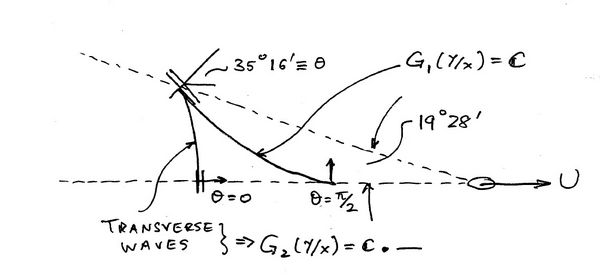
| − | + | [[Image:Kelvin_wave_image.jpg|thumb|right|600px|"transverse" and "divergent" wave systems in the Kelvin wake]] | |
The crests of the wave system trailing a ship, the Kelvin wake, are curves of constant phase of: | The crests of the wave system trailing a ship, the Kelvin wake, are curves of constant phase of: | ||
| Line 123: | Line 141: | ||
In <math> \mbox{Region I} \, </math>: | In <math> \mbox{Region I} \, </math>: | ||
| − | <center><math> \mathbf{C} = \frac{x\cos f_1(\frac{y}{x} + y\sin f_1 (\frac{y}{x})}{\cos^2 f_1 (\frac{y}{x})} \equiv G_1 (\frac{y}{x}) </math></center> | + | <center><math> \mathbf{C} = \frac{x\cos f_1(\frac{y}{x}) + y\sin f_1 (\frac{y}{x})}{\cos^2 f_1 (\frac{y}{x})} \equiv G_1 (\frac{y}{x}) </math></center> |
In <math> \mbox{Region II} \, </math>: | In <math> \mbox{Region II} \, </math>: | ||
| − | <center><math> \mathbf{C} = \frac{x\cos f_2(\frac{y}{x} + y\sin f_2 (\frac{y}{x})}{\cos^2 f_2 (\frac{y}{x})} \equiv G_2 (\frac{y}{x}) </math></center> | + | <center><math> \mathbf{C} = \frac{x\cos f_2(\frac{y}{x}) + y\sin f_2 (\frac{y}{x})}{\cos^2 f_2 (\frac{y}{x})} \equiv G_2 (\frac{y}{x}) </math></center> |
Plotting these curves we obtain a visual graph of the "transverse" and "divergent" wave systems in the Kelvin wake. | Plotting these curves we obtain a visual graph of the "transverse" and "divergent" wave systems in the Kelvin wake. | ||
| Line 137: | Line 155: | ||
[[Ocean Wave Interaction with Ships and Offshore Energy Systems]] | [[Ocean Wave Interaction with Ships and Offshore Energy Systems]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Linear Water-Wave Theory]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:37, 6 November 2010
| Wave and Wave Body Interactions | |
|---|---|
| Current Chapter | Ship Kelvin Wake |
| Next Chapter | Linear Wave-Body Interaction |
| Previous Chapter | Wavemaker Theory |
Introduction
A ship moving over the surface of undisturbed water sets up waves emanating from the bow and stern of the ship. The waves created by the ship consist of divergent and transverse waves. The divergent wave are observed as the wake of a ship with a series of diagonal or oblique crests moving outwardly from the point of disturbance. These wave were first studied by Lord Kelvin
Translating Coordinate System
We have a the standard fixed coordinate system [math]\displaystyle{ x, y, z }[/math] and a moving coordinate systems which is moving in the [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math] direction with speed [math]\displaystyle{ U }[/math]. We denote the moving coordinate systems in the [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math] direction by
Let [math]\displaystyle{ \Phi(\mathbf{x},t) \, }[/math] be the velocity potential describing the potential flow generated by the ship relative to the earth frame. The same potential expressed relative to the ship frame is [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{\Phi}(\mathbf{\bar{x}},t) \, }[/math]. The relation between the two potentials is given by the identity
where the relation between the coordinates of the two coordinate systems has been introduced. Note the time dependence occurs in two places in [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{\Phi} \, }[/math] and in one place in [math]\displaystyle{ \Phi \, }[/math]. The governing equations are always derived relative to the earth coordinate system and time derivatives are initially taken on [math]\displaystyle{ \Phi \, }[/math]. Therefore
All time derivatives of the earth fixed velocity potential [math]\displaystyle{ \Phi \, }[/math] which appear in the free surface condition and the Bernoulli equation can be expressed in terms of derivatives of [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{\Phi} \, }[/math] using the Galilean transformation derived above.
If the flow is steady relative to the ship fixed coordinate system
but
or, the ship wake is stationary relative to the ship but not relative to an observed on the beach.
Kelvin wake
Local view of Kelvin wake consists approximately of a plane progressive wave group propagating in direction [math]\displaystyle{ \theta\,\! }[/math]. As noted above surface wave systems of general form always consist of combinations of plane progressive waves of different frequencies and directions. The same model will apply to the ship kelvin wake. Relative to the earth frame, the local plane wave in Infinite Depth takes the form
Relative to the ship frame
But relative to the ship frame waves are stationary, so we must have:
or
This implies the following
- The phase velocity of the waves in the kelvin wake propagating in direction [math]\displaystyle{ \theta\, }[/math] must be equal to [math]\displaystyle{ U\cos\theta\, }[/math], otherwise they cannot be stationary relative to the ship.
- Relative to the earth system the frequency of a local system propagating in direction [math]\displaystyle{ \theta \, }[/math] is given by the relation [math]\displaystyle{ \omega = kU \cos \theta \, }[/math]
Relative to the earth system the Infinite Depth Dispersion Relation for a Free Surface states
so that
This is the wavelength of waves in a Kelvin wake propagating in direction [math]\displaystyle{ \theta \, }[/math] which are stationary relative to the ship.
Application of the Group velocity
An observer sitting on an earth fixed frame observes a local wave system propagating in direction [math]\displaystyle{ \theta\, }[/math] travelling at its group velocity [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{d\omega}{dK}\, }[/math] by virtue of the Rayleigh device which states that we need to focus on the speed of the energy density ([math]\displaystyle{ \sim \, }[/math] wave amplitude) rather than the speed of wave crests. So, relative to the earth fixed inclined coordinate system [math]\displaystyle{ (X', Y') \, }[/math]:
Or
So:
However [math]\displaystyle{ (KU\cos\theta - \omega) t =0 }[/math] so that the Rayleigh condition for the velocity of the group takes the form:
By virtue of the dispersion relation derived above:
It follows from the chain rule of differentiation that Rayleigh's condition is:
At the position of the Kelvin waves which are locally observed by an observer at the beach.
- So the "visible" waves in the wake of a ship are wave groups which must travel at the local group velocity. These conditions translate into the above equation which will be solved and discussed next. More discussion and a more mathematical derivation based on the principle of stationary phase can be found in Newman 1977.
Solution of the equation for angle
The solution of the above equation will produce a relation between [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{y}{x} \, }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \theta\, }[/math]. So local waves in a Kelvin wake can only propagate in a certain direction [math]\displaystyle{ \theta\, }[/math], given [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{y}{x} \, }[/math].
Simple algebra leads to:
which implies that
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{y}{x}(\theta) \, }[/math] is anti-symmetric about [math]\displaystyle{ \theta = 0 \, }[/math] and each part corresponds to the Kelvin wake in the port and starboard sides of the vessel. The physics on
either side is identical due to symmetry.
- [math]\displaystyle{ \theta = 0 \, }[/math]: waves propagating in the same direction as the ship. These waves can only exist at [math]\displaystyle{ Y = 0\, }[/math] as seen above.
- [math]\displaystyle{ \theta = \frac{\pi}{2} \, }[/math]: waves propagating at a [math]\displaystyle{ 90^\circ\, }[/math] angle relative to the ship direction of forward translation.
- [math]\displaystyle{ \theta = 35^\circ 16' \, }[/math]: (or 35,26°) waves propagating at an angle [math]\displaystyle{ \theta = 35^\circ 16' \, }[/math] relative to the ship axis. These are waves seen at the caustic of the Kelvin wake.
Let the solution of [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{y}{x}(\theta) \, }[/math] be of the form, when inverted:
Note that observable waves cannot exist for values of [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{y}{x}\, }[/math] that exceed the value shown in the figure or [math]\displaystyle{ \left. \frac{y}{x} \right|_{Max} = 2^{-3/2} \, }[/math]. This translates into a value for the corresponding angle equal to [math]\displaystyle{ 19^\circ 28' \, }[/math] (or 19,47°) which is the angle of the caustic for any speed [math]\displaystyle{ U\, }[/math].
The crests of the wave system trailing a ship, the Kelvin wake, are curves of constant phase of:
In [math]\displaystyle{ \mbox{Region I} \, }[/math]:
In [math]\displaystyle{ \mbox{Region II} \, }[/math]:
Plotting these curves we obtain a visual graph of the "transverse" and "divergent" wave systems in the Kelvin wake.
This article is based on the MIT open course notes and the original article can be found here
Ocean Wave Interaction with Ships and Offshore Energy Systems